모세관 레오미터
모세관 레오미터는 전단 점도 및 기타 유변학적(=유동) 특성을 측정하도록 설계된 장치입니다. 플라스틱용 모세관 레오미터는 온도 및 변형률의 함수로 고분자 용융물의 점도를 측정하도록 설계된 피스톤-다이 시스템입니다. 이들은 기본 고분자, 화합물, 작은 보강 입자 또는 섬유를 포함하는 다양한 복합 재료, 금속 사출 성형용 원료 및 유사한 재료를 테스트할 수 있습니다.
기본 원리는 열가소성 시료(원래는 과립, 분말 또는 플레이크 형태)를 가열하여 유동화시킨 다음 모세관 다이를 통해 실린더 밖으로 강제로 흐르게 하는 것입니다. 측정량은 일반적으로 정상 상태 조건에서 생성된 압력입니다. 유동 곡선은 여러 실험 데이터를 보간하여 얻어지는 일반적인 출력입니다. 점도는 그리스 문자 “에타”(η)로 표시되며 (SI 단위로) 파스칼 초(Pa·s) 또는 제곱미터당 뉴턴 초(N·s/m2)로 표현됩니다.
모세관 레오미터는 가공 조건에 실제로 부합하는 테스트 조건을 보장하며, 특히 사출 성형과 같은 고압 및 고속 기술의 경우 공정 최적화에 핵심적인 역할을 합니다.
모세관 레오미터 데이터에서 측정하거나 추정할 수 있는 다른 유변학적 특성에는 신장 점도, 압출물 팽창, 열 안정성, 벽면 미끄러짐이 있습니다. 열전도도, 압력 및 온도에 따른 밀도 의존성(pvT), 용융 강도에 대한 보조 측정을 수행할 수 있습니다.
참고 문헌
- Walters K. “Rheometry”, Chapman & Hall (1975)
- Ferry, J. D. “Viscoelastic Properties of Polymers”, John Wiley & Sons (1980)
- Dealy, J.M. and Wissbrun K.F. “Melt Rheology and its Role in Plastics Processing”, Van Nostrand Reinhold (1990), Chapman & Hall (1995)
- Macosko C.W. “Rheology – Principles, Measurements, and Applications”, Wiley-VCH (1994)
- Malkin A.Y. “Rheology – Concepts, Methods, & Applications”, ChemTec Publishing (2006)

CEAST SmartRHEO Series: Capillary Rheometer Systems
Thermoplastic materials are processed as fluids under the effect of temperature and pressure. The ability of plastics to be formed into a wide variety of shapes, by the common plastics conversion processes, has a fundamental importance in polymer science and application. The innovative Instron® line of CEAST SmartRHEO Series of Capillary Rheometer systems are designed for an accurate investigation of the rheological properties of polymeric materials.

Capillary Rheometer Systems
The innovative Instron® line of CEAST SmartRHEO Series of Capillary Rheometer systems are designed for an accurate investigation of the rheological properties of polymeric materials.
VisualRHEO | Software for CEAST SR Series Capillary Rheometers
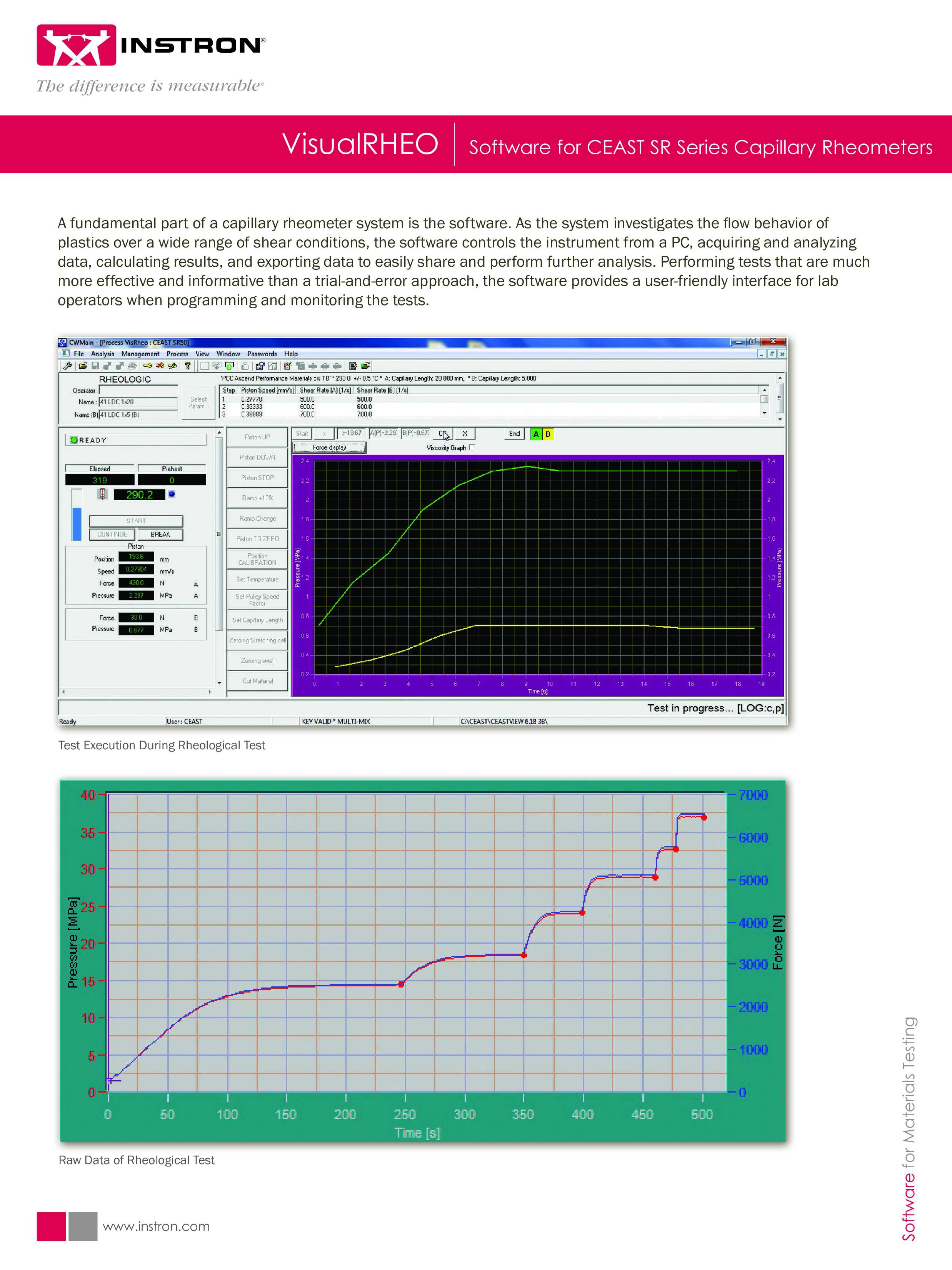
A fundamental part of a capillary rheometer system is the software. As the system investigates the flow behavior of
plastics over a wide range of shear conditions, the software controls the instrument from a PC, acquiring and analyzing
data, calculating results, and exporting data to easily share and perform further analysis. Performing tests that are much
more effective and informative than a trial-and-error approach, the software provides a user-friendly interface for lab
operators when programming and monitoring the tests.