バッテリーセパレーターの突き刺し試験
課題
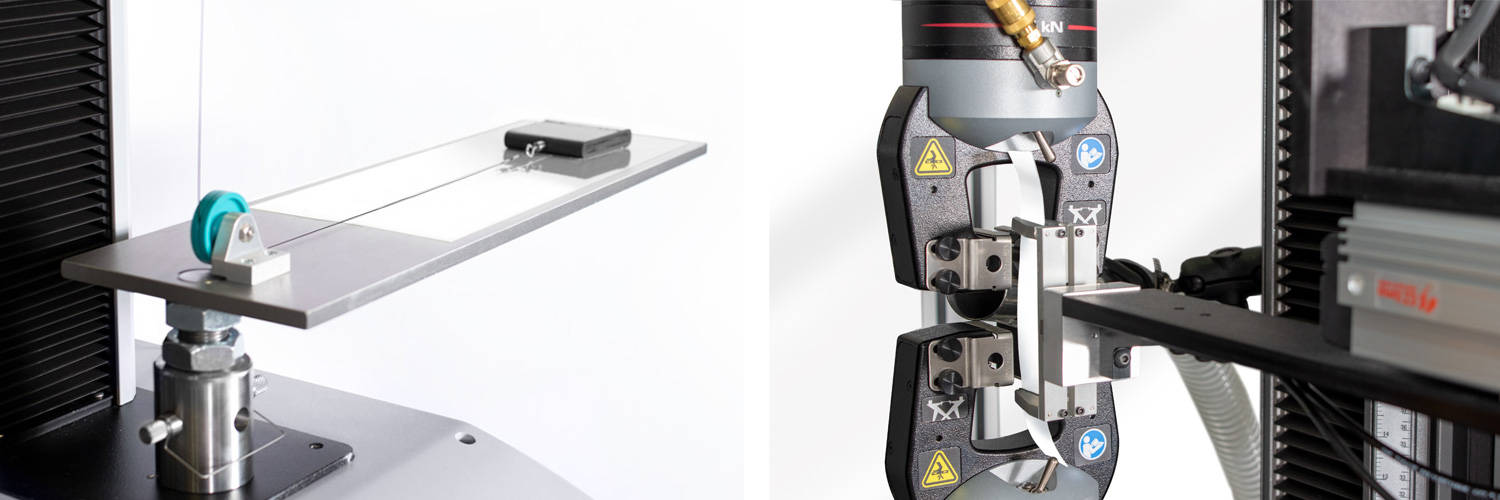
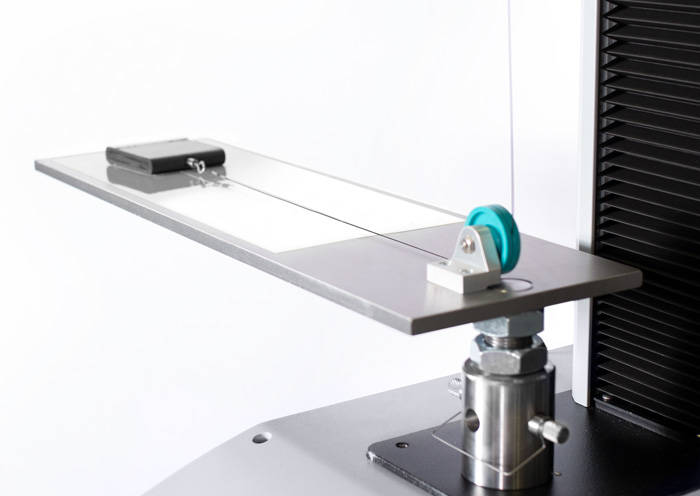
バッテリーのエネルギー密度及びサイクル寿命の改善についてポリオレフィンに対する要求は増大しています。セルセパレーター材料の選択に関する課題である、バッテリーの整合性については、内部回路のショートの潜在的危険性により、熱暴走、発火、さらには爆発に至る場合があります。衝撃に対する耐突き刺し強度の評価は、厚さ、層数および重量を減らしながら、最良の性能を有する材料を評価し、選択するために必須となる機械的特性評価です。
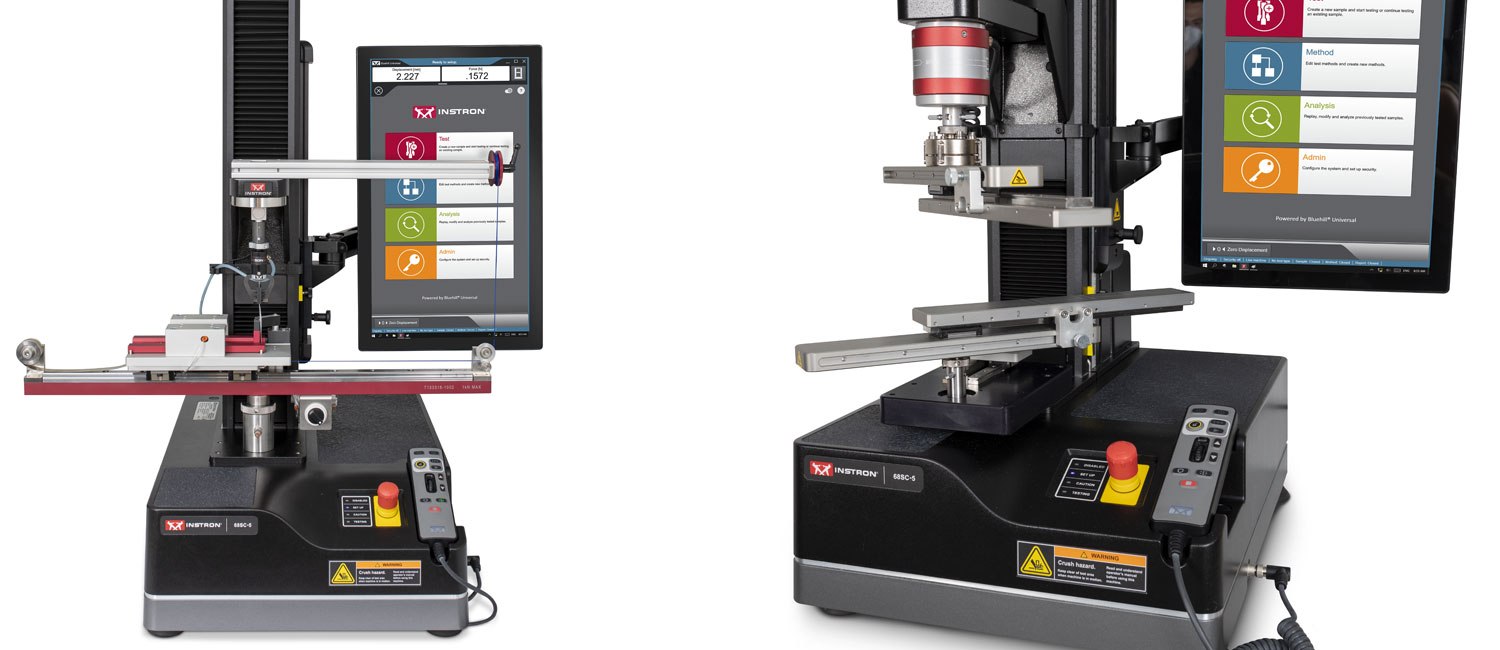
インストロンのソリューション
インストロンの9450シリーズ落錘衝撃試験機を使用し、ASTM D3763、ISO 6603またはUL2591に沿った試験を実施することで、貫通に対する耐性だけでなく、材料が耐えることのできる最大荷重および変形に関する情報が得られます。Bluehill® Impactソフトウェアは、スマートな既定値と直感的な作業工程で、力/変形曲線と材料特性をリアルタイムに表示するために、インストロン独自の認定力センサとひずみゲージまたは圧電荷重カードで構成されたアクイジションチェーンを完全に制御します。さらに、このソフトウェアは、低温でセルセパレーター材料を試験するための温度制御恒温槽をコントロールして、実際のアプリケーションをシミュレートすることができます。試験処理能力とオペレータ人数の最適化が課題である場合、インストロンは、最大30個の試験片を完全無人で、最大10本の試験片を少ないオペレーター数で試験が行えるスマートソリューションを提供いたします。これによりサイクルタイムと液体窒素の使用量を最大50%の節約できます。