Over the past 20 years, the importance of occupant protection in the development of automobiles has greatly increased. Tighter legal requirements and consumer protection programs have led to significant innovations in the area of active and passive safety. Passive safety is mainly focused on the development of methods and guidelines that reduce the severity of injuries caused by accidents.
为减轻车重、降低排放,业界正引入大量新材料,其中连续碳纤维聚合物复合材料最具轻量化潜力,但其大规模应用仍面临诸多障碍。目前复合材料部件的成本与加工周期远高于传统金属件,且需建立全新回收体系。在开发成本更低的碳纤维和热塑性基体材料方面正取得进展,这些材料不仅能加快制造流程,还便于回收利用。
Compression After Impact test (CAI) is used to define the damage resistance of composites after an Impact event. An impact on composite laminate panel may result in no visible external damage, but it may generate a dramatic reduction of compressive strength. The design of automotive parts using composite materials should consider the effects of impact on the material properties. These data can be obtained following dedicated standards (i.e. ASTM D7136M, ASTM D7136), using an Instron Drop Tower configured with CAI accessories.
In the automotive sector, development in chassis and body of vehicles is driven by two main aspects, safety, and lightweighting. As the body is the first point of impact during a car crash, modern designs have incorporated features such as crumple zone to absorb most of the initial impact, reducing the force that will reach the passengers. With this in mind, it is essential to understand material behavior under high strain rate, especially during development cycles of metals, alloys, and composites that may be used in chassis or body design. On the other hand, lightweighting provides better fuel economy for the car, decreases component wear and hence provide a much more competitive product overall. Therefore, characterizing how material properties change under high strain rate is important in order to find the optimum design maximizing safety and lightweighting.
Sheet Metal High Strain Rate Testing
The Challenge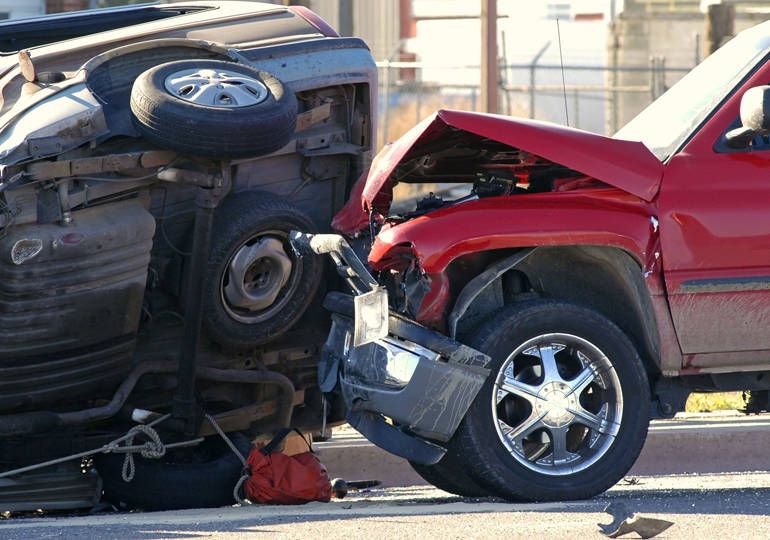
When considering the crashworthiness of components, testing in high strain rates is essential. As investigated by numerous research, mechanical properties of materials differ drastically under quasi-static conditions and high strain rates. Therefore, accurate data on strain rate dependence of material behavior will provide more realistic computer simulation and evaluation of crashworthiness of structures, whether it is during the development of new alloys or testing automotive components.
Our Solution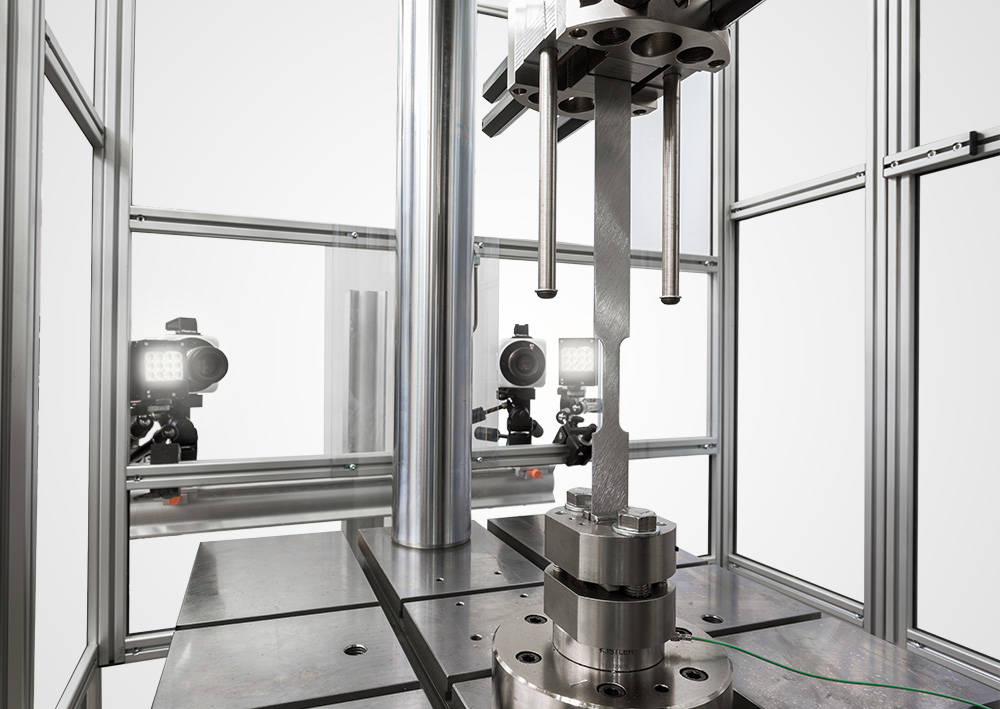
To meet the challenges of high strain rate testing, Instron has been the market leader in manufacturing high strain rate testing machines for over 20 years, advancing high strain rate research and testing capabilities on metals with suitable technologies. For testing metals and high-performance alloys, Instron offers a range of VHS systems that can perform tests that will be suited to your application up to a maximum test velocity of 25 m/s, which translates to testing conditions from quasi-static up to a strain rate of 1000/s. Instron also offers fast jaw or slack rod tensile gripping solutions to ensure gripping at test velocity and DIC integration that will provide non-contact strain measurement with the capacity for dedicated strain gauge channels.
金属的成形性对汽车制造业的发展是绝对关键的。典型成形性性能指标为塑性应变比(r值)和应变硬化指数(n值)。弯曲试验对于得出金属材料在弯曲变形过程中的成形过程和在变形过程中的破坏敏感性也很重要。
Challenge

Fahrbahnunebenheiten, Schlechtwegstrecken oder das Überfahren von z.B. Bordsteinen setzt ein Fahrzeug den unterschiedlichsten Belastungen aus. Auch Umwelteinflüsse, wie Temperatur oder Sonnenlicht können sich auf die Lebensdauer von Fahrzeugkomponenten auswirken. Die steigenden Anforderungen an Zuverlässigkeit und Komfort während einer Fahrt zwingt die Hersteller zu einer stetigen Weiterentwicklung der Fahrzeuge. Kürzere Entwicklungszeiten und die schnelle Verfügbarkeit von Testergebnissen stellt die Hersteller vor große Herausforderungen
Solution

Straßensimulatoren von Instron unterstützen den Entwicklungsprozess bereits in einer frühen Phase, um Schwachstellen von Fahrzeugkomponenten und Fahrzeugstruktur unter vertikaler Anregung zu erkennen. Hierdurch werden Erkenntnisse bezüglich Ermüdung, Komfort, Geräuschentwicklung, etc. gewonnen die zur Optimierung des Produktes benötigt werden. Mit dem Straßensimulator können hochdynamische reale und/oder synthetische Vertikalanregungen (Kräfte, Wege und Beschleunigungen) auf das Fahrzeug eingeleitet werden. Die Anregungen sind reproduzierbar und können beliebig oft wiederholt werden.
Ein effizienter Entwicklungsprozess benötigt schnelle, kostengünstige und reproduzierbare Ergebnisse im Hinblick auf Lebensdauer und Qualität des Produktes. Die Instron Straßensimulatoren sind prädestiniert solche Beanspruchungen im Labor nachzubilden und sind somit ein unverzichtbares Werkzeug im modernen und produktiven Entwicklungsprozess.
Globally, there are increasing efforts to reduce the weight of automobiles, increasing fuel efficiency which aids in the reduction of emissions. Various grades of steel have been the predominant material used for manufacturing automobiles chassis' and body. A new generation of advanced high-strength steels (AHSS) are being developed and produced to maintain the automotive industry’s demand for steel.
Despite this, automotive manufacturers are now also working with aluminum producers to increase the percentage of aluminum used in the production of automobiles. Aluminum offers low density, excellent formability, corrosion resistance, and high strength.