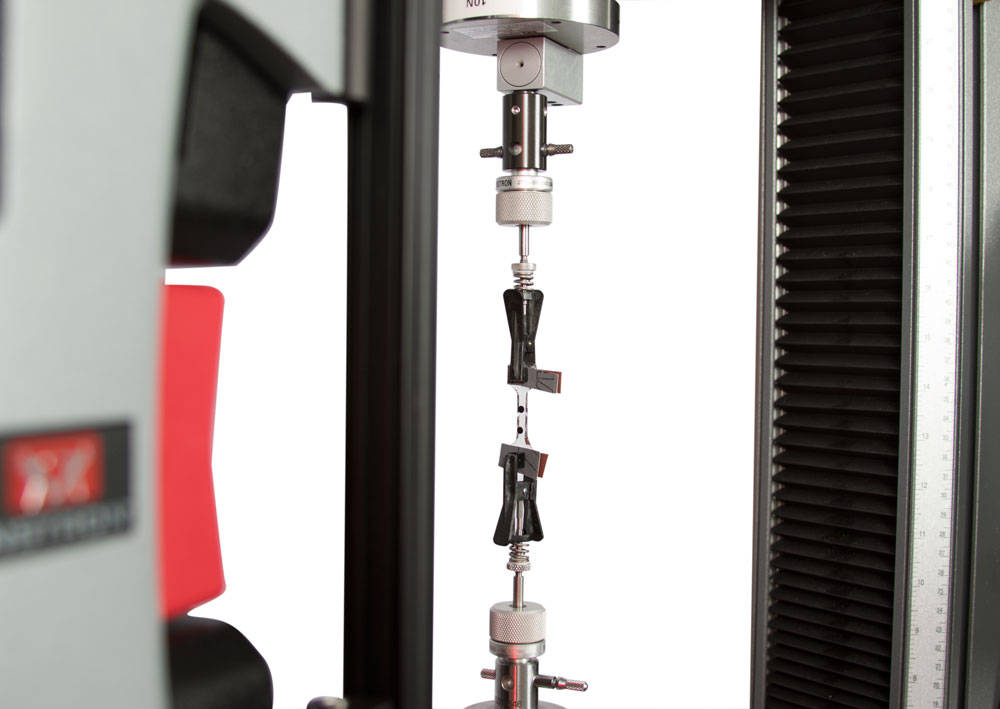
합성 박막(membrane)은 생체 의학 분야에서 일반적으로 사용됩니다. 인체의 자연 여과 시스템을 모방하기 위해 설계된 이러한 고분자 박막은 약물 전달 시스템, 의료 기기 및 인공 생체 장기에 사용하기 위하여 연구되고 또한 개발되고 있습니다.
예를 들어, 합성 박막은 신장에 이상이 있을 때 체내에서 생성된 노폐물을 제거하는 방법인 혈액 투석에 사용됩니다. 환자로부터의 혈액이 신장 투석액 (dialysis solution)에 잠긴 반투성의 박막을 통과하고, 혈액 속의 요소와 같은 노폐물이 박막을 통해서 투석액 속으로 분산됩니다.
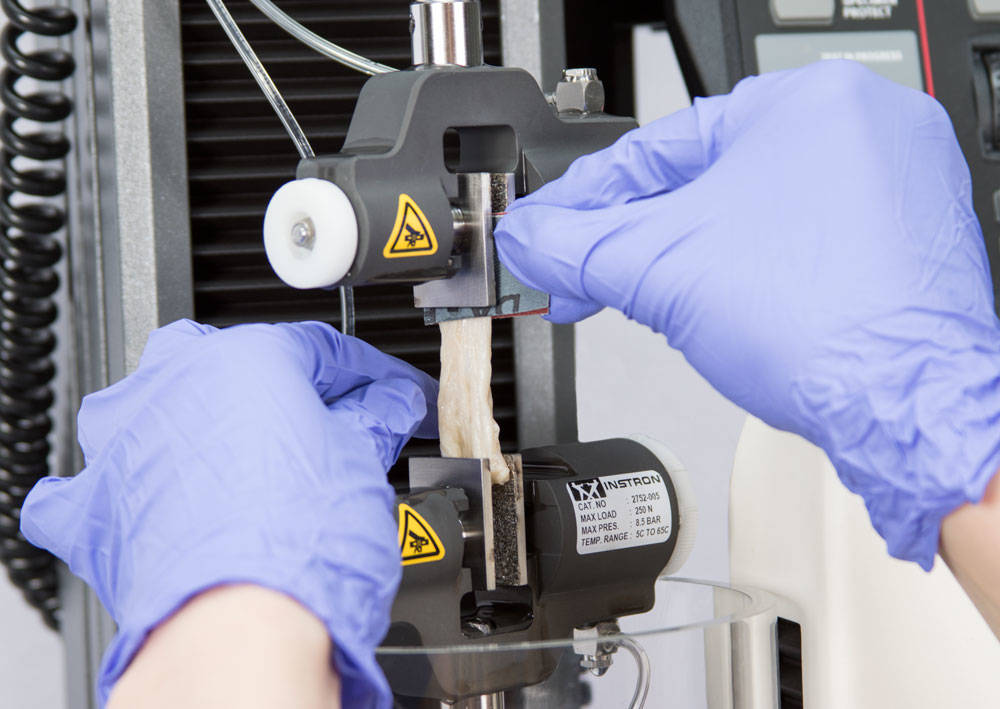
때때로 이러한 합성 박막은 습하고 미끄럽기 때문에, 이의 인장 시험은 매우 어려운 항목입니다. 부드러운 티슈의 시험과 마찬가지로, 그립 면은 박막을 견고하게 고정하기 위하여 충분한 마찰을 제공해야 할 뿐만 아니라, 시편이 찢어지는 것을 피하기 위하여 또한 충분히 섬세해야 합니다.
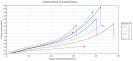
최근, 우리는 젖은 상태의 고분자 박막의 시험에 사용될 그립 방법에 대한 추천을 요청 받았습니다. 이 시험에서, 먼저 고분자 박막을 최대 20분 동안 물에 담가 두어 박막이 부드러워지고 팽창할 수 있도록 했습니다. 이 젖은 시편을 공압식 사이드 액션 그립과 고무 코팅이 된 jaw face를 갖춘 5965 dual column electromechanical machine을 이용하여 시험했습니다. 이 박막들은 아주 섬세하기 때문에 과도한 압력이 가해질 경우 그립을 닫는 과정에서 시편이 본 시험 전에 미리 손상이 될 수 있으므로 그립의 클램핑 압력을 주의하여 제어해야 합니다.
시편이 젖어있기 때문에, 부식 방지 기능의 그립이나 고정구가 사용되어야 합니다. 우리의 Bluehill® 3 Software는 시험 제어 및 결과 시험 결과를 모두 제공합니다.