Tensile Test
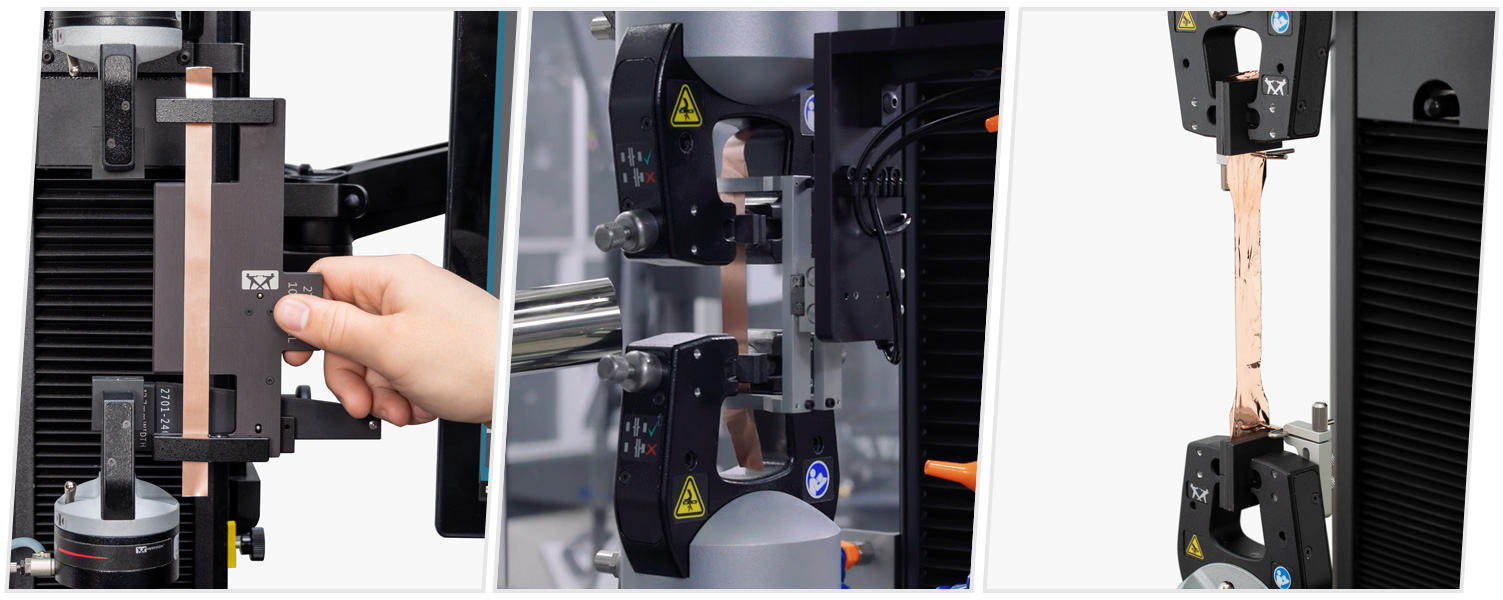
A standard tensile test is the most appropriate way to determine the mechanical properties of aluminum and copper foil specimens. Typically, elongation at break and maximum load are the key material properties that are calculated in mechanical testing, as these properties help ensure the quality of the foil; whether or not it will be able to withstand the mechanical loading and expansion/contraction in use.
While some standards may call out gripping options, such as wedge action grips, Instron has found that pneumatic side action grips are the optimal solution for foil under 20 microns thick. Pneumatic side action grips offer the ability to fine tune the clamping pressure and they will always provide constant pressure throughout each test. The use of pneumatic grips also improves throughput for these high-volume materials, as quality control labs can test hundreds of specimens per day. An additional factor that must be considered is the type of clamping surface, such as the jaw faces used. The optimal jaw faces to pair with pneumatic side action grips are rubber-coated faces. The soft and pliable rubber is able to adequately hold foil material throughout the duration of a test, while minimizing the stress concentration added by clamping the specimens.

Specimen Preparation and Alignment
Two of the biggest challenges that come from testing foil material are the preparation and alignment of the specimen. Specimen preparation is extremely critical for such fragile specimens. The better the quality of the cut, the better the quality of the edges will be for each specimen. Poorly cut edges increase the chances of the material breaking prematurely. Premature failure reduces the quality of the test results, and can lead to the need for re-testing.
Specimen alignment is also critical for repeatability and protection of the specimen, as thin foils can be noticeably affected by minor misalignment within the grips. Additionally, having to adjust foils within the grips multiple times can sometimes lead to premature breaks due to the damage caused by clamping and unclamping. We highly recommend using Instron’s Precision Specimen Loader to reduce variability in test results while improving ergonomics and safety.
Automation
Automation systems from Instron introduce a new level of productivity for foil testing. As battery production volumes continue to increase, throughput and efficiency are critical to keep up with demand. Utilizing an automation system with the recommended equipment for each application can free up operators and maximize throughput, while maintaining optimal results.





