Creep Test
What is a Creep Test?
A creep test, sometimes referred to as a stress-relaxation test, is used to determine the amount of deformation a material experiences over time while under a continuous tensile or compressive load at a constant temperature. Creep tests are fundamental for materials that are needed to withstand certain operation temperatures under load. For materials such as metals or alloys, their material properties change significantly at higher or lower temperatures. By examining the results from a creep test, engineers can determine a material's expected deformation and avoid failure when designing new systems for different environmental conditions. Creep tests are commonly performed on the following components and materials:
- Metal Working
- Springs
- Soldered Joints
- High-Temperature Materials
How to Perform a Creep Test?
To determine creep properties, a material is subjected to prolonged constant tension or compression loading at constant elevated temperature. While testing, the material's deformation is recorded at specific time intervals and overall data is plotted on a creep vs time diagram. The slope at any point on this curve is known as the creep rate, in which units are expressed in terms of in/in/hr or percent(%) elongation/hr. Maintaining a constant temperature during a creep test is critical due to the possible thermal expansion or shrinkage of the material.
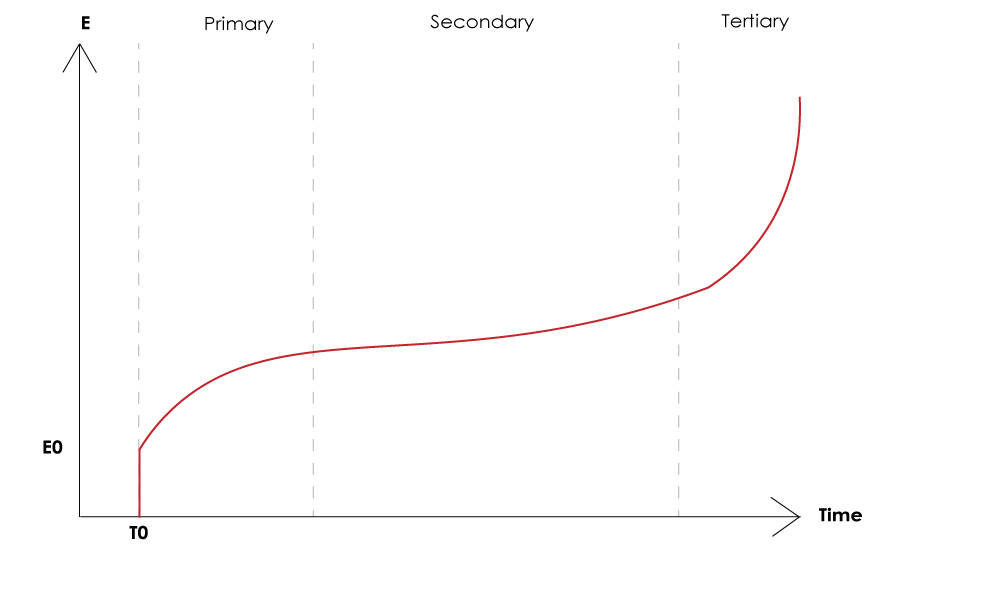
Three Stages of Creep Testing
Specimens pass through three different stages during a creep test. The first stage is primary creep, where the creep rate begins by rising quickly and then slows down and decreases. The secondary stage is where the creep rate remains fairly uniform. During the tertiary stage, when the specimen is expected to reach its breaking point, the creep rate is much steeper than it is in the secondary stage, culminating in specimen failure. If failure occurs, the time for rupture is recorded. If a specimen does not fracture within the creep test period, creep recovery may be measured.
Some examples of standards that require creep testing are ASTM E139, ASTM D2290, ASTM D2291, and ASTM D2294. For more details on testing procedures, please refer to these standards.
How to Determine Stress-Relaxation?
To determine the stress-relaxation of a material, the specimen is deformed a given amount and decrease in stress is recorded over prolonged period of exposure at constant elevated temperature. The stress-relaxation rate is the slope of the curve at any point.

Contate-nos
Fale conosco e saiba mais sobre nossas soluções para o setor e de testes. Nossas equipes de atendimento ao cliente estão à disposição e prontas para ajudar.

Brochura do Bluehill Universal
O Bluehill Universal é o software de teste de materiais avançado da Instron, projetado para interação tátil intuitiva e fluxos de trabalho simplificados. Ele oferece métodos de teste pré-carregados, QuickTest para configuração rápida, exportação de dados aprimorada e Instron Connect para comunicação direta com o serviço. Os usuários do Bluehill 2 e do Bluehill 3 podem atualizar facilmente para a versão mais recente para melhor desempenho e usabilidade

Série 3400 – Soluções de teste acessíveis
Sistemas de teste universal Instron série 3400 para testes de tração, compressão, curvatura e outros testes de propriedades de materiais.

6800 Series Premier Testing Systems Brochure
Instron 6800 Series Universal Testing Systems provide unparalleled accuracy and reliability. Built on a patent-pending Operator Protect system architecture with an all-new Smart-Close Air Kit and Collision Mitigation features, the 6800 Series makes materials testing simpler, smarter, and safer than ever before.