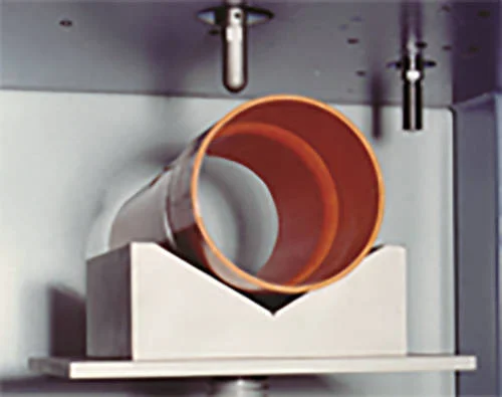
ASTM D2444 Impact Resistance of Plastic Pipe and Fittings
ASTM D2444 covers the process used to determine the resistance of thermoplastic pipe and fittings to impact by a tup (falling weight) under defined conditions. The mass of the tup shall be 6, 12, 20 or 30 lbs (2.7, 5.4, 9.1, or 13.6 kg) and shall fall from a maximum height of at least 10 ft (3.0 m) and a minimum of 2 ft (0.6 m). There are three interchangeable inserts for the tup, Type A is a cone with a rounded point, Type B is a cylinder with a relatively flat surface, and Type C has a 0.5" diameter “pin” with a rounded end. Two specimen supports (either a V-block or a Flat Plate) are defined in the standard. The combination of test variables which offers reasonably repeatable results with the test being easy to run with little or no hazard to personnel is the one that should be used.
The impact resistance of thermoplastic pipe and fittings relates to its suitability for service and to quality of the processing. It may also provide a relative measure of the tested material’s resistance to breakage during handling and installation, and in non-buried applications, to in-service breakage. Results gathered by this test can be used as the basis for establishing impact test requirements in product standards; to measure the effect of changes in materials or processing on the product and to measure any effects of the environment on the pipe or fittings.
Though the test defined in the standard calls for visual inspection after impact to determine if the specimen has failed, by including instrumentation with our Data Acquisition System, Bluehill Impact software and instrumented tup failure points/modes that may remain hidden under normal test conditions can be found. One piece of information that may not be found without the use of instrumentation is the first crack or incipient damage point. Pipes or fittings may fail in interior areas and remain undetected when visually inspected.
9400 Series Drop Tower Brochure
Instron Drop Towers are used to develop, fine tune, and validate material models. Testing materials under real impact conditions is a crucial step prior of product design. Using the characterization data obtained with the Instron 9400, coupled with customer supplied high-speed video, you can have confidence in your results and deliver new materials to your customers faster. Our Drop Tower impact systems, fixtures, and tups are designed to meet a wide range of applications and testing standards including: ISO, ASTM, ANSI, Airbus, Boeing, BSI, DIN, EN, FDA, Ford, GM, JIS, NASA, GOST, and more.
- Products
- 02/05/2020
- 763.1 KB
9400 Series Dashboard Brochure
Bluehill® Impact is built from the ground up for touch interaction. The Operator Dashboard features large touchpoints to make the user experience simpler and smarter. Easy-to-understand icons and workflows make it easy to train new or experienced users, simplify operator training, and allow you to start testing even faster than ever before
- Products
- 08/01/2019
- 2.35 MB