Within this section, we review the basics of common test types in the materials science field. Click on your test type below to learn more or visit the testing solutions library and search for specific application solutions. Also, be sure to browse our glossary for a library of terms & definitions.
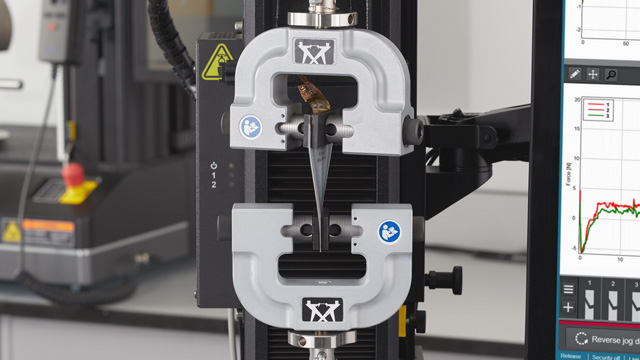
A tensile test (or tension test) applies force to a material specimen to measure the material's response to tensile (or pulling) stress. This helps product designers to decide when, where, and how to use a given material.
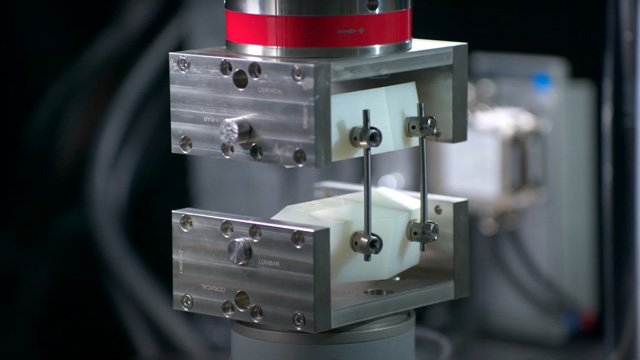
Compression tests determine a material’s behavior under applied crushing loads. They are typically conducted by applying compressive pressure to a test specimen using platens or specialized fixtures on a universal testing machine.
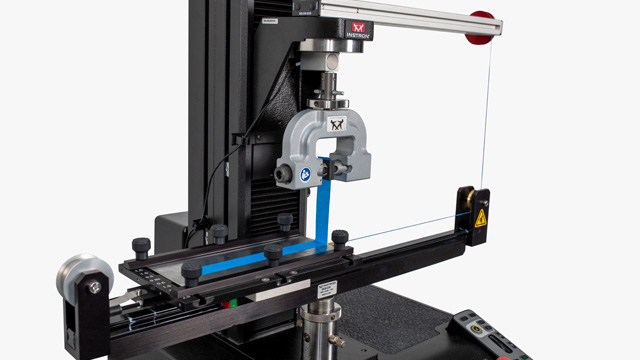
Bend testing — sometimes called flexure testing or transverse beam testing — measures the behavior of materials such as polymers, wood, and composites as they are subjected to simple beam loading.
Torsion testing evaluates the properties of materials or devices while under stress from angular displacement. It is used to test raw materials like metal wires or plastic tubing, or finished products such as screws, pharmaceutical bottles, and sheathed cables.
A dynamic testing machine performs repeated loading mechanical testing. A dynamic test machine usually stresses a material within its elastic region with cyclic loads until the specimen fails due to fatigue.
Impact testing is testing an object's ability to resist high-rate loading. An impact test determines the energy absorbed in fracturing a test piece at high velocity. Most of us think of it as one object striking another object at a relatively high speed.
HDT and Vicat tests consist of determining the temperature at which a stressed sample undergoes deflection. In the HDT test, the sample undergoes flexion, while in the Vicat test, the sample is penetrated by a point.
Rheology testing measures the deformation of matter under the influence of imposed stress, by analyzing the internal response of materials to forces. The material is forced to flow, and the rheological characteristics determine the processability.
A peel test measures the properties of an adhesive bond. It applies a tensile force to a flexible substrate that is bound by an adhesive to either another flexible substrate (such as tape, thin film, or rubber) or a rigid substrate (such as metal, rigid plastic, or composite).